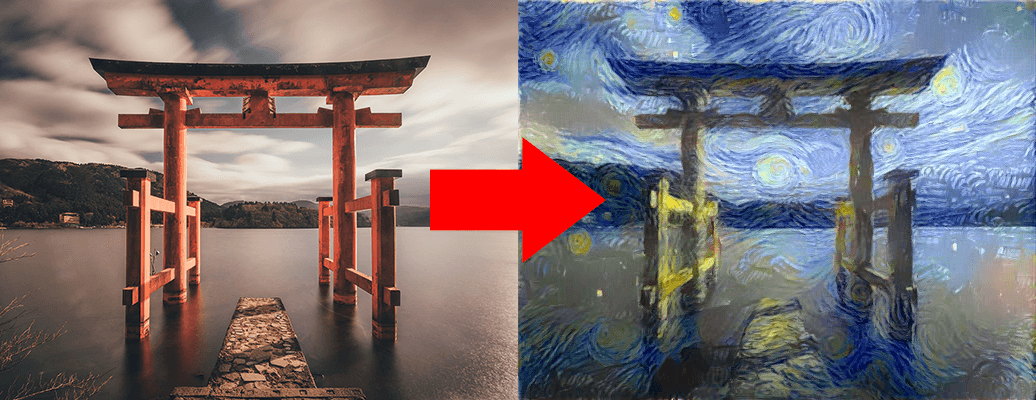
ある画像に画像のスタイル(画風)を適用した合成画像を生成するStyle TransferをPytorchで実装してみます。例のごとくGoogle Colaboratory(以下Colab)を使用しましょう。
PytorchでStyleTransferを実装して合成画像を生成する
この記事の完成品です。
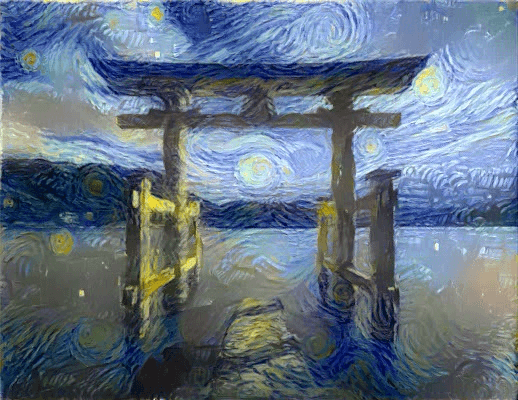
以下が元となった画像と画風の元となったゴッホの絵です。 画像はunsplashから頂きました。 鳥居の画像に上手くゴッホの画風が適用されています。

前準備
学習する前の処理を実装しましょう。
必要なライブラリとGoogleドライブのマウント
必要なライブラリをインポートしましょう。今回はGoogleドライブをマウントして、ドライブにある画像に対して学習してみます。
pytorchと画像を表示するためにPillowをインストールしましょう。
!pip install torch torchvision
!pip install Pillow==4.0.0ライブラリをインポートします。
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms, models
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npGoogleドライブをマウントします。これでColabからドライブにアクセスすることができます。
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount("/content/drive")モデルの定義
VGGを使います。deviceのgpuも定義しておきます。
vgg = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features
for param in vgg.parameters():
param.requires_grad_(False)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
vgg.to(device)画像を表示する関数を定義
画像をパスからロードしてTensorを返す関数を定義します。サイズを指定できるようにしています。
def load_image(img_path, max_size=400, shape=None):
image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
if max(image.size) > max_size:
size = max_size
else:
size = max(image.size)
if shape:
size = shape
in_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
])
image = in_transform(image).unsqueeze(0)
return image
画像を読み込んで表示する
画像のパスを定義します。ここは便宜パスを設定してください。最終的な画像のもととなる画像をcontent_pathとして、画風のもととなる画像をstyle_pathとして定義しています。
images_path ='drive/My Drive/'
content_path = images_path + 'content.jpg'
style_path = images_path + 'style.jpg'
ロードしましょう。二つの画像のサイズを合わせています。
content = load_image(content_path).to(device)
style = load_image(style_path, shape=content.shape[-2:]).to(device)Tensorからnumpyに変換して、画像を表示できるようにする関数を定義
def im_convert(tensor):
#Tensorをnp.arrayに変換する
image = tensor.to("cpu").clone().detach()
image = image.numpy().squeeze()
image = image.transpose(1,2,0)
image = image * np.array((0.5, 0.5, 0.5) + np.array((0.5, 0.5, 0.5)))
image = image.clip(0, 1)
return imageColab上に画像を表示します。
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 10))
ax1.imshow(im_convert(content))
ax1.axis("off")
ax2.imshow(im_convert(style))
ax2.axis("off")
特徴を抽出する
CNNは大きく二つの層に分かれます。画像から特徴を抜き出す前半の層と、抜き出した特徴から画像を最終的に分類する後半の層です。
二つの画像の特徴をCNNで抽出し、その特徴の差を損失関数にして最終的な画像を学習させます。
そのために画像をCNNに入れて、特定の層で特徴を抽出しましょう。VGGの0番、5番、10番、19番、21番、28番目の層で抽出します。
まず関数の定義です。
def get_features(image, model):
# Feature Extraction
# 特徴を抜き出すレイヤー
layers = {'0': 'conv1_1',
'5': 'conv2_1',
'10': 'conv3_1',
'19': 'conv4_1',
'21': 'conv4_2',
'28': 'conv5_1',}
features = {}
for name, layer in model._modules.items():
# CNNを回して
image = layer(image)
# 特定のレイヤーで特徴を抽出する
# ここでは 0番 5番 10番 19番 21番 28番
if name in layers:
features[layers[name]] = image
return features特徴を抽出しましょう。
content_features = get_features(content, vgg)
style_features = get_features(style, vgg)画風の元となる画像は単純に特徴を比較するのではなく、特徴のグラム行列を比較します。グラム行列を計算する関数を定義しましょう。
def gram_matrix(tensor):
# グラム行列を計算する
_, d, h, w = tensor.size()
tensor = tensor.view(d, h * w)
# 転置行列と行列の掛け算
gram = torch.mm(tensor, tensor.t())
return gramスタイルのグラム行列を保持する
style_grams = {layer: gram_matrix(style_features[layer]) for layer in style_features}比較する層の重みを設定します。
style_weights = {'conv1_1':1.,
'conv2_1':0.75,
'conv3_1':0.2,
'conv4_1':0.2,
'conv5_1':0.2}
content_weight = 1 #alpha
style_weight = 1e6 #blue最終的な画像はcontentの画像をコピーして学習させていくのでコピーし、targetとして定義します。
target = content.clone().requires_grad_(True).to(device)学習
準備は完了です。学習させていきましょう!途中経過を記録して後で動画にできるようにしておきます。 ハイパーパラメータを設定しましょう。
show_every = 300
optimizer = optim.Adam([target], lr=0.003)
steps = 10000
total_capture_frame_number = 500
height, width, channels = im_convert(target).shape
image_array = np.empty(shape=(total_capture_frame_number, height, width, channels))
capture_frame =steps/total_capture_frame_number
counter = 0では学習です。
for ii in range(1, steps+1):
target_features = get_features(target, vgg)
# コンテンツとの損失関数の計算
content_loss = torch.mean((target_features['conv4_2'] - content_features['conv4_2'])**2)
# スタイルとの損失関数の計算
style_loss = 0
for layer in style_weights:
target_feature = target_features[layer]
target_gram = gram_matrix(target_feature)
style_gram = style_grams[layer]
# 重み * 二乗和誤差
layer_style_loss = style_weights[layer] * torch.mean((target_gram - style_gram)**2)
_, d, h, w = target_feature.shape
style_loss += layer_style_loss / (d * h * w)
# トータルの損失関数
total_loss = content_weight * content_loss + style_weight * style_loss
optimizer.zero_grad()
total_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
#経過観察
if ii % show_every == 0:
print('Total loss: ', total_loss.item())
print('Iteration: ', ii)
plt.imshow(im_convert(target))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
# 動画用に保管
if ii % capture_frame == 0:
image_array[counter] = im_convert(target)
counter = counter + 1少し時間がかかると思います。
600回目

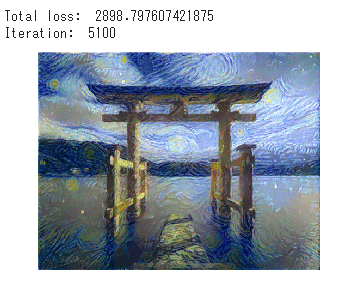
5100回目
9900回目

きちんと学習できています。
動画を書き出す
OpenCVを使って動画を作成します。
import cv2
frame_height, frame_width, _ = im_convert(target).shape
vid = cv2.VideoWriter('output.mp4', cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID'), 30, (frame_width, frame_height))
for i in range(total_capture_frame_number):
img = image_array[i]
img = img*255
img = np.array(img, dtype = np.uint8)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
vid.write(img)
vid.release()ダウンロードしましょう。
from google.colab import files
files.download('output.mp4')動画を再生すると学習過程を見ることができます。
おわりに
今回はPytorchを使ってStyle Transferを実装してみました。Google ColaboratoryのGPUを使えば簡単に試すことができます。Googleドライブの中に保存するようにすればColabのインスタンスがなくなっても大丈夫です。是非、色々他の画像を試してみてください。